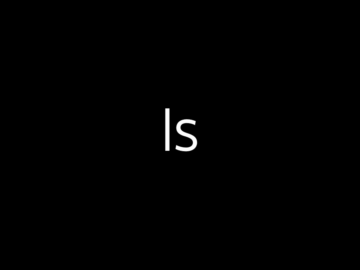whoami: The whoami command in Linux displays the username of the current user who is executing the command. It effectively answers the question, “Who am I logged in as?”
Basic Usage:
whoami: Simply typewhoamiand press Enter to see the username associated with your current session.
Example:
whoami
# Output:
# user1In this example, the command outputs user1, indicating that the current session is being run by the user user1.
The whoami command is straightforward and useful for quickly verifying your current user identity, especially in environments where you might switch between different user accounts or use sudo to execute commands as another user.